Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of type 2 diabetes mellitus among the adult residents of Tehran: Tehran Cohort Study
Background
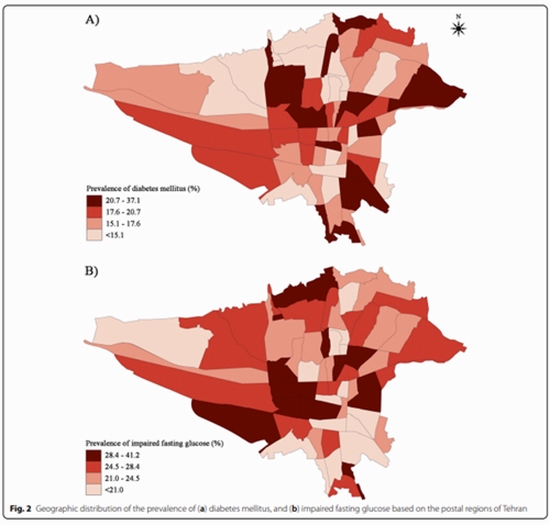
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus has increased in the past decades. We investigated the prevalence of diabetes and its awareness, treatment, and control among adult residents of Tehran.
Methods
We used the recruitment phase data of the Tehran Cohort study, enrolling a random sample of adult residents of Tehran aged ≥35 years. Diabetes was defined as self-report, current use of glucose-lowering medications, and/or fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥126mg/dl. Impaired fasting glucose (IFG) was defined as an FPG of 100-125mg/dl. Awareness was defined as diabetes self-report, treatment as receiving glucose-lowering medications, and glycemic control as FPG <126mg/dl. The age- and sex-weighted estimates were calculated using the 2016 national census. Logistic regression models were used to determine the factors associated with diabetes awareness, treatment, and control.
Conclusion
There is a high prevalence of diabetes and IFG among adult residents of Tehran. Additionally, more than two-thirds of treated diabetics living in Tehran remain uncontrolled.

.png)
.png)
ارسال نظر