مرور سیستماتیک و متاآنالیز
عوارض جانبی قلبی پس از درمانهای سلول T با گیرنده آنتی ژن کایمریک
درمان با سلول T با گیرنده آنتی ژن کایمریک (CAR) یک روش انقلابی جدید برای درمان بدخیمی های خونی مقاوم یا عودکننده است، این درمان با سندرم آزادسازی سیتوکین (CRS) و سمیت قلبی مرتبط است. از همین رو یک بررسی سیستماتیک و متاآنالیز را برای تعیین بروز و پیشبینیکنندههای حوادث قلبی عروقی (CVE) با این نوع درمان انجام شد.
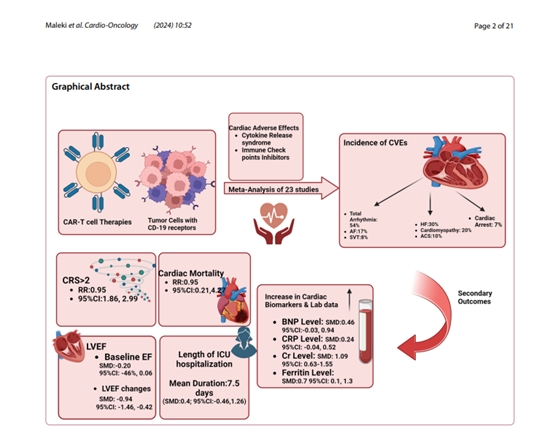
مطالعه انجام شده در Cardio-Oncology (2024) به عوارض جانبی قلبی و عروقی می پردازد که می تواند با یک درمان سرطان جدید به نام CAR T-cell therapy اتفاق بیفتد. این درمان در مبارزه با سرطان های خونی که درمان آنها سخت است بسیار خوب کرده، اما می تواند باعث ایجاد مشکلاتی در قلب شود. محققان دریافتند که بسیاری از افرادی که این درمان را انجام می دهند، مشکلات قلبی مانند ضربان قلب نامنظم، نارسایی قلبی و ضعیف شدن ماهیچه قلب دارند. آنها همچنین دریافتند افرادی که واکنش شدیدی به درمان، به نام سندرم آزادسازی سیتوکین دارند، بیشتر در معرض مشکلات قلبی هستند. حتی اگر درمان موثر و نجات دهنده باشد، مهم است که مراقب علائم ناراحتی قلبی بوده و به سرعت عوارض جانبی آن درمان شود. این مطالعه نشان میدهد که پزشکان با دقت و آمادگی پیش از اقدام به درمان، میتوانند به کاهش خطر مشکلات جدی قلبی در بیماران سرطانی که تحت درمان با CAR T-cell هستند، کمک کنند.
Cardiac adverse events after Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapies: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a new revolutionary method for treating refractory or relapsed hematologic malignancies, CAR T-cell therapy has been associated with cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and cardiotoxicity. We directed a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the incidence and predictors of cardiovascular events (CVE) with CAR T-cell therapy.
Methods: We investigated PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and ClinicalTrials.gov for studies reporting cardiovascular outcomes in CAR-T cell recipients. The study protocol was listed in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO ID: CRD42023478602). Twenty-three studies were included in this study.
Results: The pooled incidence of CVE was 54% for arrhythmias, 30% for heart failure, 20% for cardiomyopathy, 10% for acute coronary syndrome, and 7% for cardiac arrest. Patients with CVE had a higher incidence of cytokine release syndrome grade ≥ 2 (RR 2.36, 95% CI 1.86-2.99). The incidence of cardiac mortality in our meta-analysis was 2% (95% CI: 1%-3%). Left ventricular ejection fraction decline was greater in the CVE group (-9.4% versus -1.5%, p < 0.001). Cardiac biomarkers like BNP, CRP, creatinine, and ferritin were also elevated.
Conclusions: CAR T-cell therapy commonly leads to cardiotoxicity, mediated by cytokine release syndrome. Vigilant monitoring and tailored treatments are crucial to mitigate these effects. Importantly, there's no significant difference in cardiac mortality between groups, suggesting insights for optimizing preventive interventions and reducing risks after CAR T-cell therapy.
Keywords: CAR T-cell cardiotoxicity; Cancer immunotherapy; Cardiac biomarkers; Cardio-oncology; Cardiotoxicity; Cardiovascular events; Chimeric antigen receptor cardiotoxicity; Chimeric antigen receptor t-cells; Cytokine release syndrome.
© 2024. The Author(s).


.png)
.png)
ارسال نظر